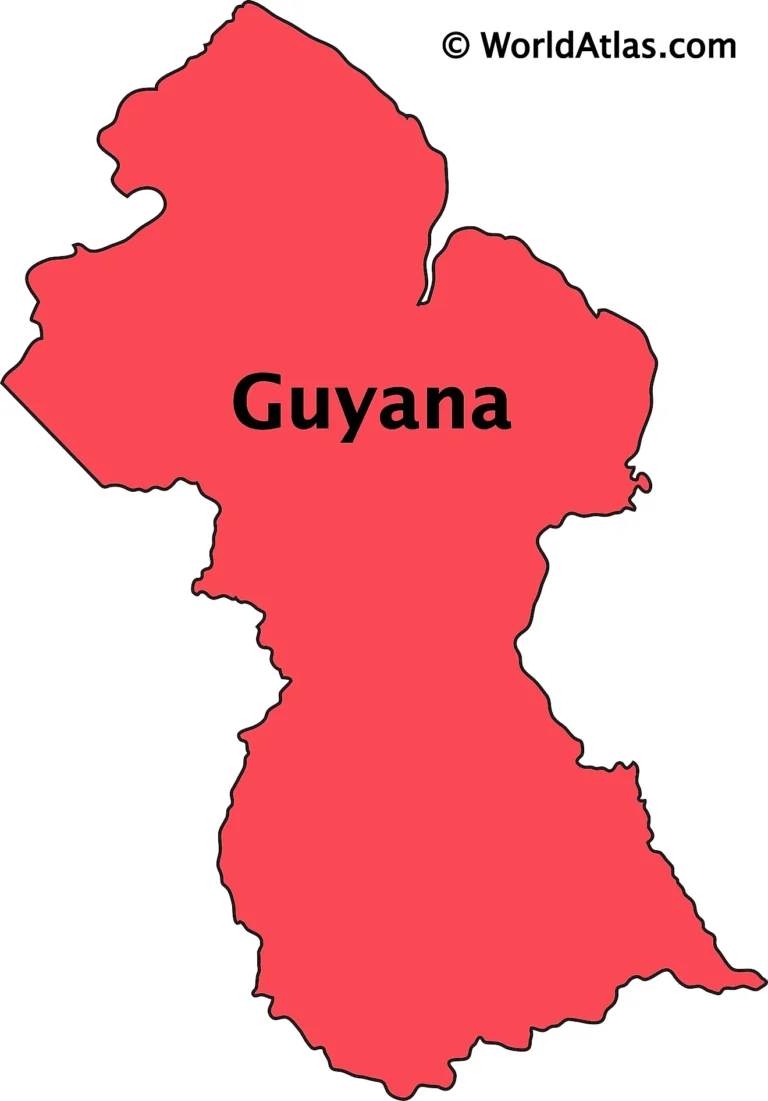
Guyana is located on the northeastern coast of South America and shares land and maritime boundaries with several countries and bodies of water. Its borders are both geographically significant and politically sensitive, especially due to longstanding territorial disputes.
Guyana’s Borders (Boundaries)
1. Northern Boundary:
- Atlantic Ocean
- Provides Guyana with a coastline of about 459 km.
- Key for shipping, fishing, oil exploration, and maritime trade.
2. Western Boundary:
- Venezuela
- Formed mainly by the Essequibo River region.
- Venezuela claims approximately two-thirds of Guyana’s territory in what is known as the Essequibo dispute.
- This is a major geopolitical issue under review by the International Court of Justice (ICJ).
3. Southern Boundary:
- Brazil
- Shared border stretches about 1,308 km long.
- Marked by forests and the Pakaraima Mountains.
- Lethem is the major border town, connected to Brazil by the Takutu River Bridge.
4. Eastern Boundary:
- Suriname
- Separated by the Corentyne River.
- There has also been a territorial dispute over the New River Triangle area, though it is currently administered by Guyana.
Summary of Guyana’s Borders
| Direction | Neighbor | Feature | Disputes |
|---|---|---|---|
| North | Atlantic Ocean | Coastline & maritime border | No major dispute |
| West | Venezuela | Essequibo region | Yes – major ongoing dispute |
| South | Brazil | Rainforest and mountains | No |
| East | Suriname | Corentyne River & New River Triangle | Yes – lesser dispute |