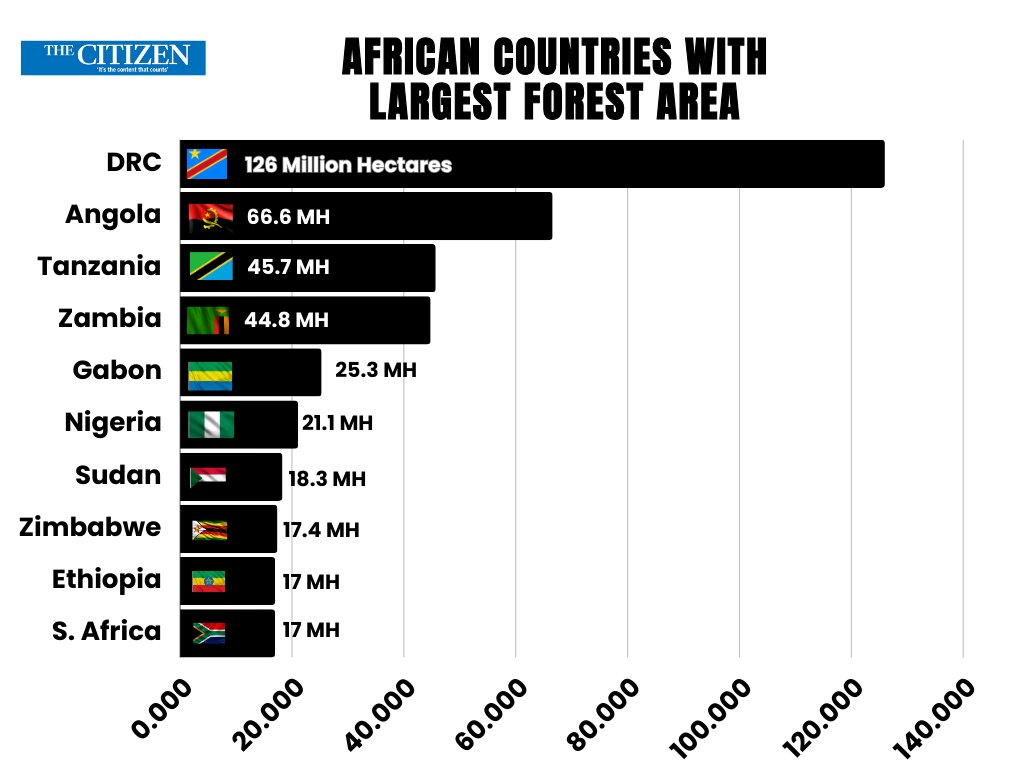
Africa is home to some of the world’s most extensive and diverse forests, ranging from tropical rainforests to dry woodlands. Forested lands play a critical role in biodiversity, climate regulation, and providing livelihoods for millions. Below is a list of African countries with significant forest cover:
1. Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC)
- Forest Land Area: Over 1.5 million km² (largest in Africa).
- Key Forests:
- Congo Basin Rainforest: The second-largest tropical rainforest in the world.
- Salonga National Park and Virunga National Park.
- Significance: A biodiversity hotspot, home to gorillas, chimpanzees, and okapi. Plays a critical role in absorbing carbon dioxide.
2. Gabon
- Forest Land Area: Approximately 85% of the country is forested.
- Key Forests:
- Loango National Park and Ivindo National Park.
- Significance: Gabon’s forests are part of the Congo Basin and are crucial for carbon storage and biodiversity.
3. Cameroon
- Forest Land Area: Over 46% of the country (around 220,000 km²).
- Key Forests:
- Congo Basin and Korup National Park.
- Significance: Known for timber exports and rich biodiversity, including forest elephants and gorillas.
4. Republic of the Congo
- Forest Land Area: Approximately 65% of the country is forested.
- Key Forests:
- Odzala-Kokoua National Park.
- Significance: Part of the Congo Basin, these forests are vital for carbon storage and habitat for endangered species.
5. Central African Republic (CAR)
- Forest Land Area: Over 36% of the country (mainly in the south).
- Key Forests:
- Dzanga-Sangha Forest Reserve.
- Significance: Home to unique species like forest elephants and pangolins.
6. Côte d’Ivoire
- Forest Land Area: Approximately 10-20%, with significant deforestation over the decades.
- Key Forests:
- Taï National Park and Banco National Park.
- Significance: Hosts remnants of the Upper Guinean Rainforest, a critical biodiversity area.
7. Ghana
- Forest Land Area: About 20% of the country.
- Key Forests:
- Ankasa Conservation Area and Kakum National Park.
- Significance: Part of the West African rainforest belt, known for timber and cocoa farming impacts.
8. Liberia
- Forest Land Area: Over 40% of the country.
- Key Forests:
- Sapo National Park.
- Significance: Contains some of the last remaining parts of the Upper Guinean Rainforest.
9. Madagascar
- Forest Land Area: Approximately 20%, though heavily threatened by deforestation.
- Key Forests:
- Rainforests of Atsinanana and Masoala National Park.
- Significance: Unique biodiversity with endemic species like lemurs, chameleons, and baobab trees.
10. Mozambique
- Forest Land Area: Around 40% of the country is forested.
- Key Forests:
- Miombo woodlands and Gorongosa National Park.
- Significance: Known for tropical hardwoods and diverse ecosystems.
11. Tanzania
- Forest Land Area: Approximately 40% of the country.
- Key Forests:
- Eastern Arc Mountains, Selous Game Reserve, and Mount Kilimanjaro forests.
- Significance: Miombo woodlands dominate, alongside coastal and montane forests.
12. Angola
- Forest Land Area: About 47% of the country.
- Key Forests:
- Miombo woodlands and Mayombe Forest.
- Significance: Rich in tropical hardwoods and a critical carbon sink.
13. Zambia
- Forest Land Area: Around 66% of the country.
- Key Forests:
- Miombo woodlands and Kafue National Park.
- Significance: Home to critical woodlands supporting diverse wildlife and rural livelihoods.
14. Guinea
- Forest Land Area: Around 26% of the country.
- Key Forests:
- Ziama and Mount Nimba forest reserves.
- Significance: Part of the Upper Guinean Forest, hosting rare plant and animal species.
15. South Sudan
- Forest Land Area: Over 37% of the country.
- Key Forests:
- Boma National Park and Bandingilo National Park.
- Significance: Rich in savannah woodlands and tropical forests.
16. Equatorial Guinea
- Forest Land Area: About 58% of the country.
- Key Forests:
- Monte Alen National Park.
- Significance: Pristine rainforests with diverse flora and fauna.
17. Uganda
- Forest Land Area: Around 24% of the country.
- Key Forests:
- Bwindi Impenetrable Forest and Mabira Forest.
- Significance: Home to mountain gorillas and other endangered species.
18. Sierra Leone
- Forest Land Area: Approximately 28% of the country.
- Key Forests:
- Gola Rainforest National Park.
- Significance: Critical for biodiversity and environmental conservation.
19. Ethiopia
- Forest Land Area: Around 15%, but heavily impacted by deforestation.
- Key Forests:
- Bale Mountains and Harenna Forest.
- Significance: Montane forests with unique endemic species.
20. Malawi
- Forest Land Area: About 34% of the country.
- Key Forests:
- Mulanje Mountain Forest Reserve and Nyika National Park.
- Significance: Miombo woodlands and montane forests dominate.
Challenges Facing African Forests:
- Deforestation: Driven by agriculture, logging, and urbanization.
- Climate Change: Impacts rainfall patterns and forest health.
- Illegal Logging: Threatens biodiversity and sustainability.
- Conservation Needs: Many forests are underprotected and vulnerable to exploitation.